Page 74 - Journal of Library Science in China 2020 Vol.46
P. 74
CHEN Geng & HU Yachun / The attribution analysis of low participation in public reading 073
among rural residents: A survey from 77 administrative villages and rural libraries in Hubei Province
development, 31.2% “relatively important”, 27.2% “moderate”, 11.2% “not that important” and
5.5% “not important at all”. There is a direct positive correlation between reading cognition and
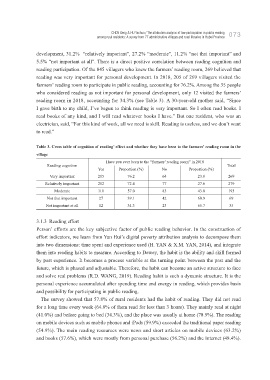
reading participation. Of the 845 villagers who knew the farmers’ reading room, 269 believed that
reading was very important for personal development. In 2018, 205 of 269 villagers visited the
farmers’ reading room to participate in public reading, accounting for 76.2%. Among the 35 people
who considered reading as not important for personal development, only 12 visited the farmers’
reading room in 2018, accounting for 34.3% (see Table 3). A 30-year-old mother said, “Since
I gave birth to my child, I’ve begun to think reading is very important. So I often read books. I
read books of any kind, and I will read whatever books I have.” But one resident, who was an
electrician, said, “For this kind of work, all we need is skill. Reading is useless, and we don’t want
to read.”
Table 3. Cross table of cognition of reading’ effect and whether they have been to the farmers’ reading room in the
village
Have you ever been to the “farmers’ reading room” in 2018
Reading cognition Total
Yes Proportion (%) No Proportion (%)
Very important 205 76.2 64 23.8 269
Relatively important 202 72.4 77 27.6 279
Moderate 110 57.0 83 43.0 193
Not that important 27 39.1 42 60.9 69
Not important at all 12 34.3 23 65.7 35
3.1.3 Reading effort
Person’ efforts are the key subjective factor of public reading behavior. In the construction of
effort indicators, we learn from Yan Hui’s digital poverty attribution analysis to decompose them
into two dimensions: time spent and experience used (H. YAN & X.M. YAN, 2014), and integrate
them into reading habits to measure. According to Dewey, the habit is the ability and skill formed
by past experience. It becomes a process variable at the turning point between the past and the
future, which is phased and adjustable. Therefore, the habit can become an active structure to face
and solve real problems (R.D. WANG, 2019). Reading habit is such a dynamic structure. It is the
personal experience accumulated after spending time and energy in reading, which provides basis
and possibility for participating in public reading.
The survey showed that 57.8% of rural residents had the habit of reading. They did not read
for a long time every week (64.8% of them read for less than 3 hours). They mainly read at night
(41.0%) and before going to bed (34.3%), and the place was usually at home (78.9%). The reading
on mobile devices such as mobile phones and iPads (59.9%) exceeded the traditional paper reading
(54.9%). The main reading resources were news and short articles on mobile devices (63.2%)
and books (57.6%), which were mostly from personal purchase (56.2%) and the Internet (48.4%).