Page 194 - Journal of Library Science in China, Vol.47, 2021
P. 194
ZHANG Wei, WANG Hao, DENG Sanhong & ZHANG Baolong / Sentiment term extraction 193
and application of Chinese ancient poetry text for digital humanities
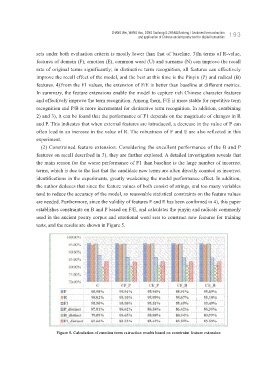
sets under both evaluation criteria is mostly lower than that of baseline. 3)In terms of R-value,
features of domain (F), emotion (E), common word (U) and surname (N) can improve the recall
rate of original terms significantly; in distinctive term recognition, all features can effectively
improve the recall effect of the model, and the best at this time is the Pinyin (P) and radical (B)
features. 4)From the F1 values, the extension of F/E is better than baseline at different metrics.
In summary, the feature extensions enable the model to capture rich Chinese character features
and effectively improve the term recognition. Among them, F/E is more stable for repetitive term
recognition and P/B is more incremental for distinctive term recognition. In addition, combining
2) and 3), it can be found that the performance of F1 depends on the magnitude of changes in R
and P. This indicates that when external features are introduced, a decrease in the value of P can
often lead to an increase in the value of R. The robustness of F and E are also reflected in this
experiment.
(2) Constrained feature extension. Considering the excellent performance of the B and P
features on recall described in 3), they are further explored. A detailed investigation reveals that
the main reason for the worse performance of F1 than baseline is the large number of incorrect
terms, which is due to the fact that the candidate new terms are often directly counted as incorrect
identifications in the experiments, greatly weakening the model performance effect. In addition,
the author deduces that since the feature values of both consist of strings, and too many variables
tend to reduce the accuracy of the model, so reasonable statistical constraints on the feature values
are needed. Furthermore, since the validity of features F and E has been confirmed in 4), this paper
establishes constraints on B and P based on F/E, and calculates the pinyin and radicals commonly
used in the ancient poetry corpus and emotional word sets to construct new features for training
tests, and the results are shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Calculation of emotion term extraction results based on constraint feature extension