Page 141 - JOURNAL OF LIBRARY SCIENCE IN CHINA 2018 Vol. 42
P. 141
140 Journal of Library Science in China, Vol. 8, 2016
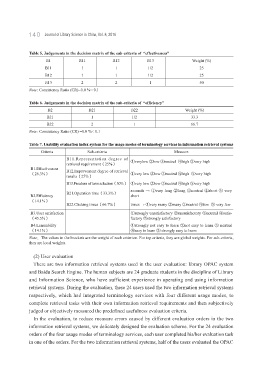
Table 5. Judgements in the decision matrix of the sub-criteria of “effectiveness”
B1 B11 B12 B13 Weight (%)
B11 1 1 1/2 25
B12 1 1 1/2 25
B13 2 2 1 50
Note: Consistency Ratio (CR)=0.0 %< 0.1
Table 6. Judgements in the decision matrix of the sub-criteria of “efficiency”
B2 B21 B22 Weight (%)
B21 1 1/2 33.3
B22 2 1 66.7
Note: Consistency Ratio (CR) =0.0 %< 0.1
Table 7. Usability evaluation index system for the usage modes of terminology services in information retrieval systems
Criteria Sub-criteria Measure
B11.Representation degree of ①verylow ②low ③neutral ④high ⑤very high
retrieval requirement(25%)
B1.Effectiveness B12.Improvement degree of retrieval
(26.3%) ①very low ②low ③neutral ④high ⑤very high
results(25%)
B13.Freedom of term selection(50%) ①very low ②low ③neutral ④high ⑤very high
seconds → ①very long ②long ③neutral ④short ⑤ very
B2.Efficiency B21.Operation time(33.3%) short
(14.1%)
B22.Clicking times(66.7%) times → ①very many ②many ③neutral ④few ⑤ very few
B3.User satisfaction ①strongly unsatisfactory ②unsatisfactory ③neutral ④satis-
(45.5%) factory ⑤strongly satisfactory
B4.Learnability ①strongly not easy to learn ②not easy to learn ③ neutral
(14.1%) ④easy to learn ⑤ strongly easy to learn
Note:The values in the brackets are the weight of each criterion. For top criteria, they are global weights. For sub-criteria,
they are local weights.
(2) User evaluation
There are two information retrieval systems used in the user evaluation: library OPAC system
and Baidu Search Engine. The human subjects are 24 graduate students in the discipline of Library
and Information Science, who have sufficient experience in operating and using information
retrieval systems. During the evaluation, these 24 users used the two information retrieval systems
respectively, which had integrated terminology services with four different usage modes, to
complete retrieval tasks with their own information retrieval requirements and then subjectively
judged or objectively measured the predefined usefulness evaluation criteria.
In the evaluation, to reduce measure errors caused by different evaluation orders in the two
information retrieval systems, we delicately designed the evaluation scheme. For the 24 evaluation
orders of the four usage modes of terminology services, each user completed his/her evaluation task
in one of the orders. For the two information retrieval systems, half of the users evaluated the OPAC