Page 134 - JOURNAL OF LIBRARY SCIENCE IN CHINA 2018 Vol. 42
P. 134
OU Shiyan, TANG Zhengui & SU Feifei / Construction and usage of terminology services for information retrieval 133
terminology service, whereas the precision of the rest two third of the experiments decreases. No
matter precision increases or decreases, its variation amplitude is not big and only fluctuates within
a small range. After an analysis, we found that the difference in precision variations is caused
because: expanding query terms through the terminology service makes the number of retrieved
documents and the number of relevant documents among the retrieval documents both increase,
and the increase magnitude of these two numbers determines the variation of prevision.
As two important evaluation measures of retrieval results, precision and recall complement each
other and also restrict each other. Evaluating each of them respectively cannot comprehensively
reflect the change in the performance of an information retrieval system. Thus we used the F value
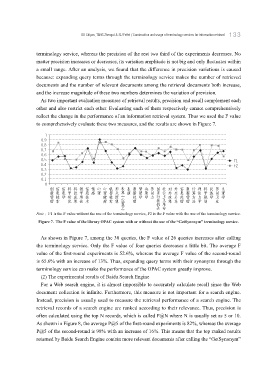
to comprehensively evaluate these two measures, and the results are shown in Figure 7.
'
'
᛫
ѹ η η ሙ ሙ ஔ η ৱ ॷ ॷ ॎ ៶ ᛫ ኮ х ҷ ڎ ᇫ ࠫ ܱ η ᝠ ေ ሙ ඟ ҷ ၷ
ழ ৌ ৌ ߦ ߦ ৌ ਖ ေ ေ ٨ र Ἧ ေ ኖ ү ࠒ ͘ ܱ ̔ ৌ ካ ߦ ீ ү ေ
ኮ ೝ ߦ ᆑ ੇ ေ Ϥ ೝ ॷ ေ ܫ ߦ ߦ ҧ ᛡ ˟ Т ܫ ኮ வ ҧ ߦ Ӽ ߦ
ေ ጊ ቃ ౧ ష क ጊ ᣤ ߦ ေ ˧ ኖ ጇ ေ ေ ข ߦ ѳ ၷ
ἰ ᭩
Т ֑
Note:F1 is the F value without the use of the terminology service, F2 is the F value with the use of the terminology service.
ฌ' ˞ళΎၹషឦҬᄊϙὊ' ˞ΎၹషឦҬᄊϙ
Figure 7. The F value of the library OPAC system with or without the use of the “GetSynonym” terminology service.
As shown in Figure 7, among the 30 queries, the F value of 26 queries increases after calling
the terminology service. Only the F value of four queries decreases a little bit. The average F
value of the first-round experiments is 52.6%, whereas the average F value of the second-round
is 65.6% with an increase of 13%. Thus, expanding query terms with their synonyms through the
terminology service can make the performance of the OPAC system greatly improve.
(2) The experimental results of Baidu Search Engine
For a Web search engine, it is almost impossible to accurately calculate recall since the Web
document collection is infinite. Furthermore, this measure is not important for a search engine.
Instead, precision is usually used to measure the retrieval performance of a search engine. The
retrieval records of a search engine are ranked according to their relevance. Thus, precision is
often calculated using the top N records, which is called P@N where N is usually set as 5 or 10.
As shown in Figure 8, the average P@5 of the first-round experiments is 82%, whereas the average
P@5 of the second-round is 98% with an increase of 16%. This means that the top ranked results
returned by Baidu Search Engine contain more relevant documents after calling the “GetSynonym”