Page 114 - Journal of Library Science in China, Vol.45, 2019
P. 114
CHEN Bikun, ZHOU Huixian, ZHONG Zhouyan & WANG Yuefen / Exploring the user platform preference and 113
user interest preference of Chinese scholarly articles: A comparison based on usage metrics
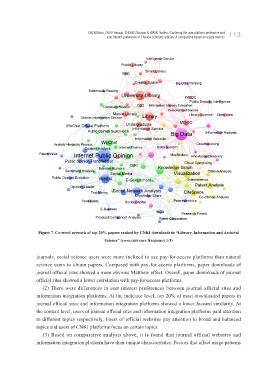
Figure 7. Co-word network of top 20% papers ranked by CNKI downloads in “Library, Information and Archival
Science” (co-occurrence frequency≥3)
journals, social science users were more inclined to use pay-for-access platforms than natural
science users to obtain papers. Compared with pay-for-access platforms, paper downloads of
journal official sites showed a more obvious Matthew effect. Overall, paper downloads of journal
official sites showed a lower correlation with pay-for-access platforms.
(2) There were differences in user interest preferences between journal official sites and
information integration platforms. At the indicator level, top 20% of most downloaded papers in
journal official sites and information integration platforms showed a lower Jaccard similarity. At
the content level, users of journal official sites and information integration platforms paid attention
to different topics respectively. Users of official websites pay attention to broad and balanced
topics and users of CNKI platforms focus on certain topics.
(3) Based on comparative analysis above, it is found that journal official websites and
information integration platform have their unique characteristics. Factors that affect usage patterns