Page 122 - Journal of Library Science in China, Vol.45, 2019
P. 122
ZHANG Chengzhi, LI Zhuo, ZHAO Mengyuan, LIU Jiahao & ZHOU Qingqing / Citing behavior of Chinese books based on citation content 121
intuitive. Catalini et al. (2015) analyzed full-texts of 15,731 articles in the Journal of Immunology
and found that 4,888 articles contained negative citations. There were 18,304 negative citations
(accounting for 2.4%) in 762,355 citation contents of 15,731 articles, and about 7.1% of 146,891
references were cited negatively at least once.
It can be seen that citation sentiment analysis based on citation contexts can significantly
improve accuracy of the citation sentiment recognition. In addition, negative citations may be
ignored based on machine annotation, as most citations are neutral. Therefore, this paper used a
manual method to annotate sentiment of citation contents.
2 Research methods
2.1 Analytical framework
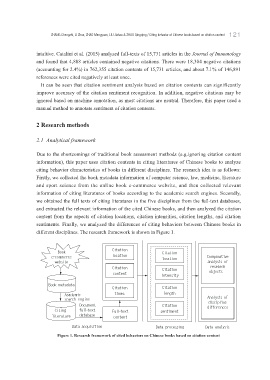
Due to the shortcomings of traditional book assessment methods (e.g.ignoring citation content
information), this paper uses citation contents in citing literatures of Chinese books to analyze
citing behavior characteristics of books in different disciplines. The research idea is as follows:
Firstly, we collected the book metadata information of computer science, law, medicine, literature
and sport science from the online book e-commerce website, and then collected relevant
information of citing literatures of books according to the academic search engines. Secondly,
we obtained the full texts of citing literatures in the five disciplines from the full-text databases,
and extracted the relevant information of the cited Chinese books, and then analyzed the citation
content from the aspects of citation locations, citation intensities, citation lengths, and citation
sentiments. Finally, we analyzed the differences of citing behaviors between Chinese books in
different disciplines. The research framework is shown in Figure 1.
$JUBUJPO
#PPL $JUBUJPO
F DPNNFSDF MPDBUJPO MPDBUJPO $PNQBSBUJWF
XFCTJUF BOBMZTJT PG
$JUBUJPO $JUBUJPO SFTFBSDI
DPOUFOU PCKFDUT
JOUFOTJUZ
#PPL NFUBEBUB
$JUBUJPO $JUBUJPO
"DBEFNJD UJNFT MFOHUI
TFBSDI FOHJOF "OBMZTJT PG
EJTDJQMJOF
%PDVNFOU $JUBUJPO EJGGFSFODFT
$JUJOH GVMM UFYU 'VMM UFYU TFOUJNFOU
MJUFSBUVSF EBUBCBTF DPOUFOU
%BUB BDRVJTJUJPO %BUB QSPDFTTJOH %BUB BOBMZTJT
Figure 1. Research framework of cited behaviors on Chinese books based on citation content