Page 73 - JOURNAL OF LIBRARY SCIENCE IN CHINA 2018 Vol. 42
P. 73
072 Journal of Library Science in China, Vol. 8, 2016
In the analysis of causes of ICT device usage status of rural residents, we picked series of
variables related with subjective perceptions as intermediate variables. Except perceived ICT
usefulness, perceived ease of ICT use and perceived self-efficacy of ICT learning, perceived
information needs of rural residents have effects on their using behaviors. The agents of
information behavior are always situated in anomalous state of knowledge (ASK) (Belkin, Oddy,
& Brooks, 1982), and perceive their information needs in a blurry way. Hence, their information
seeking behaviors are limited to their perceived or expressive information needs, not the actual
information demands, and place restrictions on their choices and usage of information seeking
tools. Different categories of rural residents represent diverse perceived information needs because
of their age and careers. Younger and no-farming residents usually reach out from limitations of
traditional agricultural context to richer social resources, and their perceived information needs are
more colorful and diverse. Therefore, they are less inclined to suffer digital poverty. In contrast,
older rural residents are more likely to be suppressed by life pressure and land with a slow pace
of life; their social activities tend to be simpler; and their perceptions of information needs are
possibly simplified. In turn, they own limited subjective needs on ICT learning and usage. Table 5
sums up the typical descriptions of ICT perceptions by rural digitally poor communities.
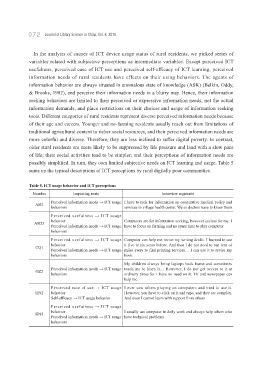
Table 5. ICT usage behavior and ICT perceptions
Number Impacting route Interview segments
Perceived information needs → ICT usage I have to seek for information on cooperative medical policy and
AH2
behaviors services in village health center. We as doctors have to know them
Perceived usefulness → ICT usage
behavior Computers are for information seeking, however useless for me. I
AH23
Perceived information needs → ICT usage have to focus on farming and no spare time to play computer
behaviors
Perceived usefulness → ICT usage Computer can help me revise my writing drafts. I learned to use
behavior it five to six years before. And thus I do not need to run tens of
CQ1
Perceived information needs → ICT usage miles away to find printing services… I can use it to revise my
behaviors book
My children always bring laptops back home and sometimes
Perceived information needs → ICT usage teach me to learn it… However, I do not get access to it at
GZ2
behaviors ordinary times for I have no need on it. TV and newspaper can
help me
Perceived ease of use → ICT usage I ever saw others playing on computers and tried to use it.
HN2 behavior However, you have to click on it and type, and they are complex.
Self-efficacy → ICT usage behavior And even I cannot learn with support from others
Perceived usefulness → ICT usage
behavior I usually use computer in daily work and always help others who
HN5
Perceived information needs → ICT usage have technical problems
behaviors