Page 146 - Journal of Library Science in China, Vol.47, 2021
P. 146
CAI Yingchun / Digital humanities evaluation: discipline, professionalism and technicality 145
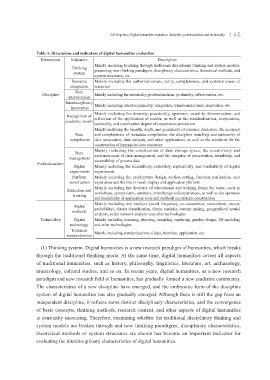
Table 1. Dimensions and indicators of digital humanities evaluation
Dimensions Indicators Description
Mainly including breaking through traditional disciplinary thinking and system models,
Thinking presenting new thinking paradigms, disciplinary characteristics, theoretical methods, and
system
system structures, etc.
Resource Mainly including the authoritativeness, rarity, completeness, and systematicness of
integration resources
Data
Discipline Mainly including the rationality, professionalism, profundity, effectiveness, etc.
interpretation
Interdisciplinary Mainly including interdisciplinarity, integration, transboundariness, innovation, etc.
innovation
Mainly including the diversity, practicality, openness, sociality, dissemination, and
Recognition of
academic results reflection of the application of results, as well as the standardization, cooperation,
rationality, and contribution degree of cooperation annotation
Mainly including the breadth, depth, and granularity of resource disclosure, the accuracy
Data and completeness of metadata compilation, the discipline matching and rationality of
compilation data association, data analysis, and other applications, as well as the standards for the
construction of humanities data resources
Mainly including the construction of data storage space, the scientificity and
Data
management systematicness of data management, and the integrity of preservation, storability, and
accessibility of process data
Professionalism
Digital Mainly including the scientificity, suitability, replicability, and verifiability of digital
experiments experiments
Platform Mainly including the architecture design, section setting, function realization, user
construction experience and the like in result display and application platform
Mainly including the diversity of educational and training forms for users, such as
Education and workshops, symposiums, seminars, interchange and experiences, as well as the openness
training
and learnability of application tools and methods in platform construction
Mainly including text analysis (word frequency, co-occurrence, association, vector,
Digital
methods probability), cluster classification, theme analysis, content mining, geographical spatial
analysis, social network analysis and other technologies
Technicality Digital Mainly including scanning, shooting, sampling, capturing, graphic design, 3D modeling
technology and other technologies
Technical
standardization Mainly including standardization of data, interface, application, etc.
(1) Thinking system. Digital humanities is a new research paradigm of humanities, which breaks
through the traditional thinking mode. At the same time, digital humanities covers all aspects
of traditional humanities, such as history, philosophy, linguistics, literature, art, archaeology,
musicology, cultural studies, and so on. In recent years, digital humanities, as a new research
paradigm and new research field of humanities, has gradually formed a new academic community.
The characteristics of a new discipline have emerged, and the embryonic form of the discipline
system of digital humanities has also gradually emerged. Although there is still the gap from an
independent discipline, it reflects some distinct disciplinary characteristics, and the convergence
of basic concepts, thinking methods, research content, and other aspects of digital humanities
is constantly increasing. Therefore, examining whether the traditional disciplinary thinking and
system models are broken through and new thinking paradigms, disciplinary characteristics,
theoretical methods or system structures are shown has become an important indicator for
evaluating the interdisciplinary characteristics of digital humanities.