Page 115 - JOURNAL OF LIBRARY SCIENCE IN CHINA 2018 Vol. 42
P. 115
114 Journal of Library Science in China, Vol. 8, 2016
For example, cross-coordination relations can be transformed to hierarchical relations between
extended concepts and core concepts.
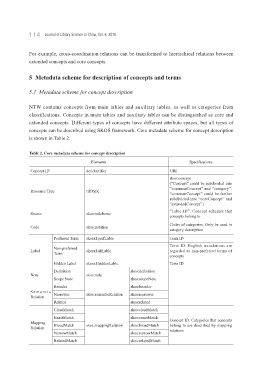
5 Metadata scheme for description of concepts and terms
5.1 Metadata scheme for concept description
NTW contains concepts from main tables and auxiliary tables, as well as categories from
classifications. Concepts in main tables and auxiliary tables can be distinguished as core and
extended concepts. Different types of concepts have different attribute spaces, but all types of
concepts can be described using SKOS framework. Core metadata scheme for concept description
is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Core metadata scheme for concept description
Elements Specifications
Concept ID dc:identifier URI
skos:concept
(“Concept” could be subdivided into
“commonConcept” and “category”.
Resource Type rdf:type
“commonConcept” could be further
subdivided into “coreConcept” and
“extendedConcept” )
“Table ID”. Concept schemes that
Source skos:inScheme
concepts belong to
Codes of categories. Only be used in
Code skos:notation
category description
Preferred Term skosxl:prefLable Term ID
Term ID. English translations are
Non-preferred
Label skosxl:altLable regarded as non-preferred terms of
Term
concepts
Hidden Label skosxl:hiddenLable Term ID
Definition skos:definition
Note skos:note
Scope Note skos:scopeNote
Broader skos:broader
Semantic Narrower skos:semanticRelation skos:narrower
Relation
Related skos:related
CloseMatch skos:closeMatch
ExactMatch skos:exactMatch
Mapping BroadMatch skos:mappingRelation skos:broadMatch Concept ID. Categories that concepts
belong to are described by mapping
Relation relations
NarrowMatch skos:narrowMatch
RelatedMatch skos:relatedMatch